Aerial mapping has revolutionized industries from construction to environmental monitoring, providing detailed and accurate representations of the Earth’s surface. Among the most common techniques for aerial mapping are LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) scanning and photogrammetry. Each of these technologies has its own set of advantages and use cases, and choosing between them depends on several factors, such as the type of project, accuracy requirements, and environmental conditions.
In this blog, we’ll delve into the differences between LiDAR scan and photogrammetry, highlighting their strengths and limitations to help you determine the best suited for your aerial mapping needs.
What is LiDAR scanning?
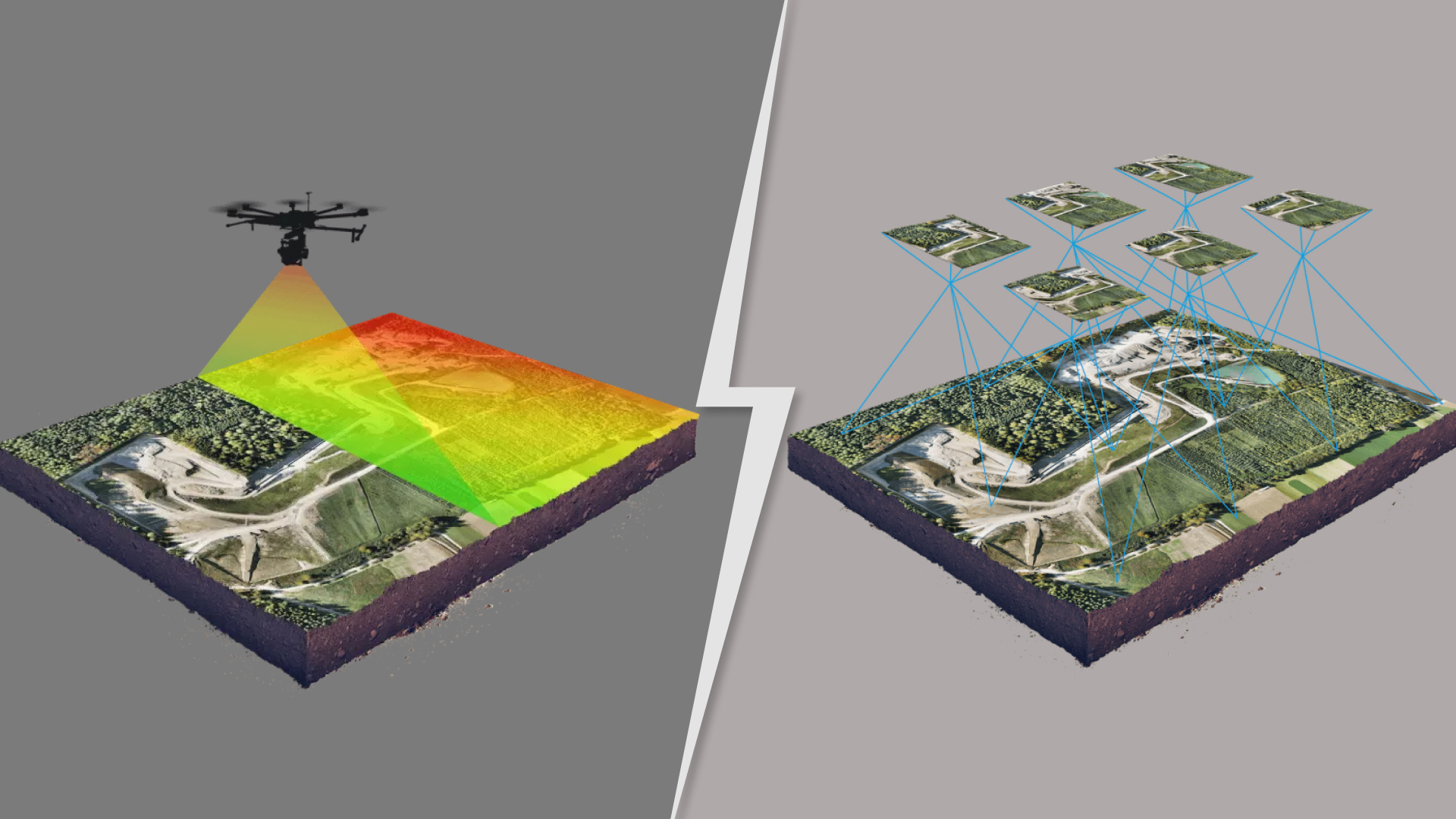
LiDAR scanning uses laser technology to measure distances between the sensor (typically mounted on an aircraft or drone) and the surface below. The LiDAR sensor emits rapid pulses of laser light, which bounce off the ground or other objects and return to the sensor.
These returns are then processed to create a detailed 3D point cloud, which can be converted into precise maps, 3-D models, terrain models, and LiDAR scan to BIM services. This integration allows for accurate and efficient 3D modeling of existing structures and environments, enhancing projects’ design, construction, and maintenance phases with highly detailed, data-rich models that reflect real-world conditions.
Key Benefits of LiDAR:
- High Accuracy: LiDAR provides accurate elevation data and can penetrate through vegetation, making it ideal for mapping forests, hilly terrains, and other obstructed environments.
- Faster Data Collection: LiDAR can quickly gather large amounts of data, making it suitable for large-scale projects.
- Works in Low Visibility Conditions: Unlike photogrammetry, LiDAR does not depend on visible light, making it effective in low-light or cloudy conditions.
Limitations of LiDAR:
- Higher Cost: LiDAR equipment tends to be more expensive, and the data processing can also be resource-intensive.
- Limited Detail in Visual Mapping: LiDAR excels at capturing elevation and distance but does not capture the colour or texture of the objects, which may be necessary for some projects.
When to Use LiDAR for Aerial Mapping?
- Large-scale topographic mapping and surveying
- Forestry management and vegetation analysis
- Construction and infrastructure planning, including road and railway projects
- Areas with dense vegetation or challenging terrains
- Projects requiring precise elevation and contour data
What is Photogrammetry?
Photogrammetry, conversely, involves capturing high-resolution photographs from the air using drones or aircraft and then using specialized software to process these images into maps and 3D models. Photogrammetry can extract spatial data to create highly detailed visual models by comparing overlapping images from different angles.
Key Benefits of Photogrammetry:
- High-Resolution Imagery: Photogrammetry produces highly detailed and visually rich maps, making it ideal for projects that require texture and colour information, such as architectural modelling and land use analysis.
- Cost-Effective: Compared to LiDAR, photogrammetry tends to be less expensive and is often more affordable for smaller projects or those on a budget.
- Versatility: It can be used for various mapping purposes, including terrain, infrastructure, and landscape.
Limitations of Photogrammetry:
- Requires Clear Weather Conditions: Photogrammetry depends on visible light and clear skies, making it less reliable in poor weather conditions or low-light environments.
- Limited in Vegetated Areas: Photogrammetry struggles to provide accurate data for heavily vegetated areas as the camera may not capture the ground beneath the trees and shrubs.
LiDAR vs Photogrammetry: Which One Is Better for Aerial Mapping?
To determine which technology is best suited for your aerial mapping project, it’s essential to consider the specific requirements of your task. Here’s a breakdown of key factors to help you choose between LiDAR and photogrammetry:
Terrain and Vegetation Coverage
- LiDAR: Ideal for mapping areas with dense vegetation, such as forests or jungles, as it can penetrate the canopy to capture the ground surface.
- Photogrammetry: Less practical in areas with thick vegetation, as it relies on visible light to capture data and may struggle to see beneath the tree cover.
Accuracy Requirements
- LiDAR: Offers superior accuracy, especially for capturing elevation data. If your project requires precise height, slope, or terrain modelling measurements, LiDAR is likely the better choice.
- Photogrammetry: While photogrammetry can provide detailed surface models, it may not always meet the high precision required for specific engineering or surveying applications.
Budget Considerations
- LiDAR: LiDAR equipment and processing software costs are high. If you have a large budget for your aerial mapping project, this technology may be worth the investment for its accuracy and efficiency.
- Photogrammetry: Photogrammetry is often more affordable, making it an excellent choice for smaller projects or those with budget constraints. Many drones used for photogrammetry are also significantly cheaper than LiDAR systems.
Weather and Light Conditions
- LiDAR: Works well in various lighting and weather conditions, including cloudy or rainy days. It’s an excellent option for projects where environmental conditions may not always be ideal.
- Photogrammetry: Requires good weather and lighting conditions for optimal image quality. Cloudy or overcast days can make it difficult to achieve clear photographs, affecting the quality of the final map or model.
Data Processing
- LiDAR: The data processing for LiDAR is typically more complex and can require specialized software and computing power to process the point cloud data.
- Photogrammetry: Photogrammetry requires substantial processing power but is generally less complex than LiDAR, especially if the mapped area is relatively small.
When to Use Photogrammetry for Aerial Mapping?
- Real estate and architectural projects that require high-resolution imagery
- Land use and urban planning
- Cultural heritage documentation and 3D modelling
- Small to medium-sized projects with limited budget
- Areas with clear weather and minimal vegetation
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Technology for Your Project
Both LiDAR scanning and photogrammetry offer unique advantages for aerial mapping, and choosing between the two depends on the specific needs of your project. If you require highly accurate elevation data or if you’re working in a challenging environment with dense vegetation, LiDAR may be the better option. However, photogrammetry is a strong contender for detailed visual representations and more budget-friendly options.
Ultimately, the best choice depends on your project’s goals, environmental factors, and budget. Consider consulting with an aerial mapping expert to determine which technology will provide the most accurate and effective results for your needs.

Recent Comments