LiDAR technology has revolutionized the way we capture and analyze detailed information about structures, particularly historical sites. It provides highly accurate and comprehensive data, enhancing the detail level in as-built BIM models. This offers numerous benefits for preserving and restoring historical sites.
What is LiDAR?
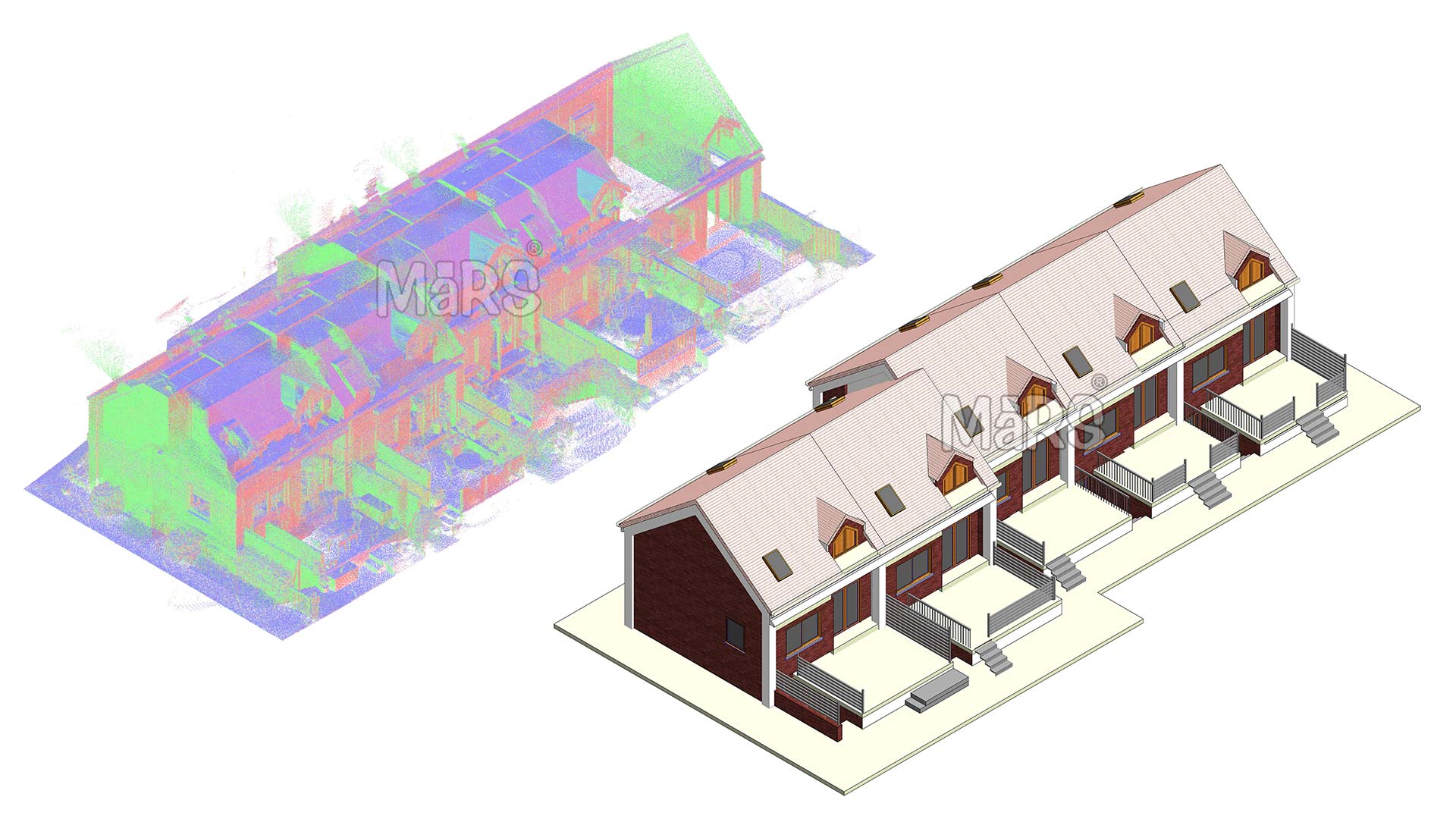
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a remote sensing technology that measures distances using laser pulses. It involves emitting laser beams towards a target, which reflect back to the sensor. By calculating the time it takes for the pulses to return, it determines the distance to the surface, creating a “point cloud” of data points. This data is used to produce detailed 3D models and maps of the scanned area. This is widely used in topographic mapping, forestry, archaeology, urban planning, and environmental monitoring due to its high accuracy and ability to capture complex details.
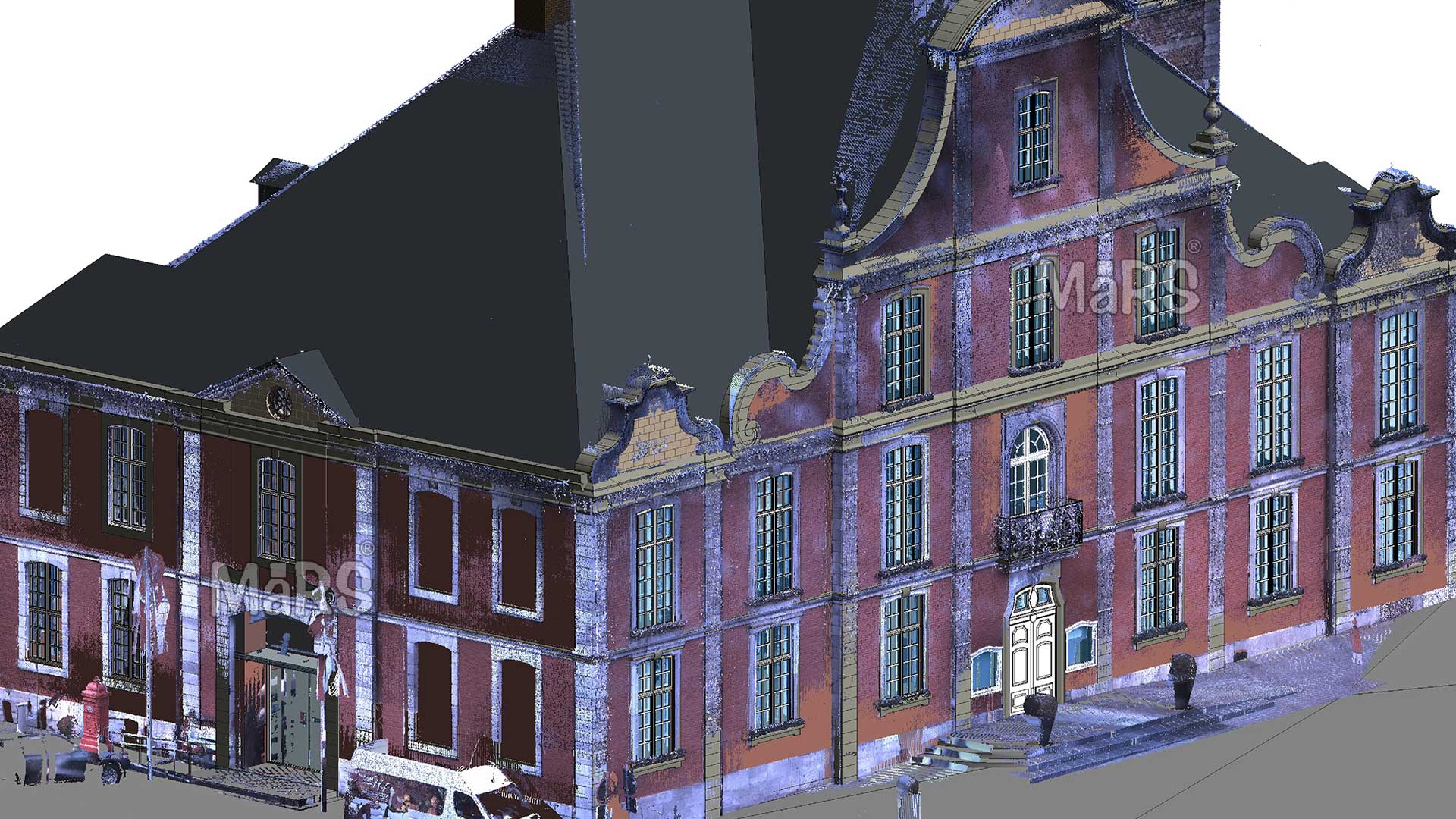

Importance of LiDAR to as-built BIM models for historical sites
1. High-Resolution Data Capture
LiDAR technology uses laser pulses to measure distances between the sensor and various points on a surface. pilgrThis results in the collection of high-resolution point clouds that accurately represent the geometry of the historical site. Unlike traditional surveying methods, which may rely on manual measurements and less precise tools, it captures every detail with exceptional accuracy. The high-resolution data enables the creation of detailed BIM models that reflect the true dimensions, shapes, and features of the historical site. This level of detail is crucial for accurately documenting and analyzing complex historical structures.
2. Comprehensive 3D Models
One of the primary advantages of Light Detection and Ranging is its ability to produce comprehensive 3D models of historical sites. The point cloud data collected by LiDAR Scan to Revit Modeling can be converted into detailed 3D models that include not only the building’s exterior but also its interior elements. This holistic view is particularly beneficial for historical sites with intricate architectural details, hidden spaces, or complex geometries. The resulting BIM models offer a complete and accurate representation of the site, facilitating better planning and execution of restoration and preservation efforts.
3. Preservation of Fine Details
Historical sites often feature intricate architectural elements, such as decorative carvings, ornate moldings, and unique structural components. LiDAR technology excels at capturing these fine details with high precision. Accurately recording every nuance and feature ensures that these elements are preserved in the as-built BIM model. This detailed documentation is essential for maintaining the historical and cultural significance of the site, allowing restorers to replicate original features accurately and preserve the site’s authenticity.
4. Efficient Data Collection
This technology offers significant advantages in terms of efficiency compared to traditional methods. LiDAR scanners can quickly cover large areas and capture vast amounts of data in a short period of time. This efficiency is particularly valuable for historical sites that are difficult to access or require extensive documentation. Reducing the time and effort required for data collection allows for faster creation of detailed BIM models, accelerating the overall restoration process and minimizing disruptions to the site.
5. Accurate Condition Assessment
In addition to capturing detailed geometry, LiDAR technology can help assess the condition of historical sites. The high-resolution point clouds allow for precise measurements of structural elements, enabling the identification of any deterioration, deformation, or damage. This information is crucial for planning effective restoration strategies and addressing areas that require immediate attention. By providing an accurate assessment of the site’s condition, technology supports informed decision-making and enhances the overall effectiveness of restoration efforts.
6. Integration with Historical Data
LiDAR can be integrated with existing historical data, such as architectural drawings, photographs, and historical records. By combining scanned data with these sources, it is possible to create a more complete and accurate BIM model of the historical site. This integration allows for a detailed comparison between the current state of the site and its historical design, helping to identify changes and plan restoration work that aligns with the original intent of the structure.
7. Enhanced Visualization and Analysis
The detailed 3D models generated by LiDAR technology offer enhanced visualization and analysis capabilities. Restoration experts, architects, and historians can use these models to explore different aspects of the site, simulate restoration scenarios, and visualize how changes will affect the overall structure. This advanced visualization helps in communicating restoration plans to stakeholders and the public, facilitating better understanding and support for preservation efforts.
8. Long-Term Documentation and Monitoring
LiDAR technology provides a permanent digital record of historical sites that can be used for long-term documentation and monitoring. As-built BIM models created from Laser scanning data serve as a valuable resource for future reference, allowing for ongoing assessment and monitoring of the site’s condition over time. This long-term documentation supports proactive maintenance and helps ensure the continued preservation of the historical site.
Key benefits of using LiDAR technology for creating detailed BIM models of historical buildings
- LiDAR scanning captures complex architectural details and geometries, enabling highly detailed BIM models that accurately represent the as-built conditions of historical structures.
- LiDAR-generated BIM models offer detailed, data-rich documentation for historical sites, facilitating restoration, maintenance, and preservation with easy access to critical historical information.
- Analyzing BIM models helps restoration professionals identify structural issues and deterioration, guiding effective decision-making and preservation of historical integrity.
- LiDAR-based BIM models enable virtual tours of historical sites, enhancing public appreciation and understanding, especially when physical access is restricted.
- Integrating point cloud data into BIM software transforms point clouds into parametric models with geometric, material, and historical details, a process known as Historical Building Information Modeling (HBIM) for heritage structures.
Every laser pulse tells a story. Capture it all with LiDAR and convert it to a detailed 3D model. Preserve heritage in high definition with LiDAR Scan to BIM technology.
Conclusion
LiDAR technology enhances the detail level in as-built BIM models for historical sites. It provides high-resolution data, comprehensive 3D models, and precise documentation of fine details. Its efficient data collection, ability to assess site conditions, and integration with historical data make it invaluable for restoring and preserving historical sites. By using this technology, restoration experts can create accurate and detailed BIM models. These models support effective preservation strategies and safeguard our cultural heritage for future generations.


Recent Comments