LiDAR Scanning
What is LiDAR Scanning?
LiDAR(Light Detection and Ranging) scanning is a remote sensing technology. It uses laser beams for capturing detailed measurements of objects, surfaces, or environments. It takes for laser beams to reflect off an object and return to the sensor by measuring the time that helps to create highly accurate 3D models. LiDAR is used in fields such as building construction, surveying, environmental monitoring, and autonomous vehicles. A growing application of LiDAR scanning is its integration with the BIM process that helps how buildings and infrastructure projects are designed and managed.
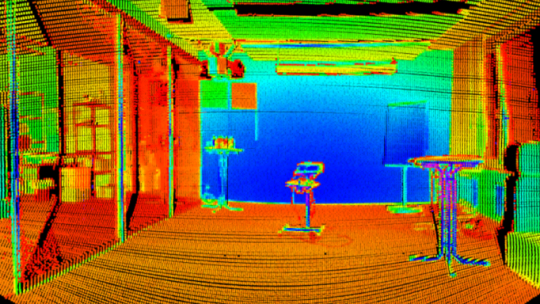
How LiDAR Scanning Works
LiDAR scanning uses laser beams that reflect off surfaces, and the time of flight (ToF) is used to calculate distances. Modern LiDAR scanners can emit up to 1 million laser beams per second to create a detailed 3D point cloud. This data is integrated with GPS and Inertial Measurement Units (IMU) to ensure detailed mapping, even in complex or large environments. The resulting point cloud forms a detailed model that can be used for design, analysis, and documentation in BIM systems.
Types of LiDAR
Terrestrial LiDAR: This type is set up on the ground often mounted on tripods. It’s perfect for scanning buildings, roads, and landscapes. Terrestrial LiDAR helps to create accurate as-built models and makes it easier to manage and document construction projects.
Aerial LiDAR: Mounted on drones or aircraft, aerial LiDAR is designed for scanning large areas like cities, forests, or infrastructure projects. This method is especially useful for integrating data into BIM for large-scale planning, such as urban development or environmental assessments.
Mobile LiDAR: As the name suggests, this type is attached to moving vehicles which allows for real-time data capture while on the go. It’s great for mapping roads and infrastructure, and the models generated can integrate into BIM software for effective maintenance planning.
LiDAR and Scan-to-BIM
As-Built Documentation: LiDAR scanning captures the exact details of existing structures. which can be compared to the original design. This allows for detailed as-built models in BIM which are important for renovations, retrofits, and facility management.
Clash Detection: When new designs are integrated into existing structures, the LiDAR-generated point cloud can be used in BIM to check for clashes between new elements and existing components. This process helps error mitigation before the construction process, saving time and costs.
Renovation and Retrofitting: LiDAR scanning helps in renovating older buildings or upgrading infrastructure. BIM models can be developed to plan upgrades or retrofits without needing extensive manual measurements by capturing the exact dimensions of the building.
Facility Management: After the construction process, LiDAR scans of the final build can be imported into BIM to serve as a reference for maintenance and operations. The digital twin created from LiDAR data allows facility managers to track building conditions and plan future modifications efficiently.
Application of LiDAR Scanning
Construction and Infrastructure
LiDAR scanning helps build detailed 3D models of construction sites and structures. These models are used in BIM to make sure designs are correct, track progress, and catch any mistakes early. It also helps monitor projects in real-time.
Surveying and Mapping
Surveyors use LiDAR to create accurate maps of land and check sites. When combined with BIM, LiDAR data shows the landscape and terrain clearly, which is helpful for planning big projects.
Environmental Monitoring
LiDAR is important for understanding natural areas. It can map things like coastal erosion, forests, and lakes, and this information is useful for projects that need to think about their impact on the environment.
Benefits of LiDAR Scanning
- LiDAR collects data without touching the objects. This means there’s less chance of damage and allows safe measurements in delicate or risky places.
- LiDAR captures a lot of data in one scan, producing very detailed images. This level of detail shows small features and changes in the landscape that other methods might miss.
- Aerial LiDAR can see through tree branches and thick leaves, allowing accurate ground mapping even in forests. This is especially helpful in forestry and environmental studies.
- Mobile LiDAR systems gather data while moving, making them great for capturing busy environments like crowded roads or changing landscapes without stopping anything.
- LiDAR creates detailed 3D models right from the data, making it easier to visualize and analyze structures and landscapes compared to 2D methods.
- LiDAR can be used in many weather conditions and settings, making it useful for challenging projects, whether in cities, rural areas, or industrial sites.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
LiDAR sends out laser beams that bounce off objects and come back. By timing how long it takes, we can figure out how far away things are and create a 3D picture of the area.
LiDAR is used in many areas, like construction, road mapping, environmental research, and self-driving cars. It helps us plan and manage projects more accurately.
LiDAR gives very accurate measurements, which helps construction teams avoid mistakes. This can save time and money by catching problems early.
LiDAR scans capture the exact details of buildings. This makes it easier to plan renovations or upgrades because you don’t need to measure everything by hand.
Once a building is done, LiDAR can create a digital version of the building (a "digital twin"). This helps building managers keep track of maintenance and plan future changes.
Yes! LiDAR can be used to check if new designs fit with existing buildings. It helps catch issues early, so you don’t run into problems during construction.
LiDAR can be costly, but it usually saves money in the long run because it helps avoid mistakes and speeds up construction planning.
LiDAR is very accurate, often measuring within millimeters. This makes it a great tool for projects that need exact details, like construction or environmental work.
