Drone Mapping
What is Drone Mapping?
Drone mapping (or surveying) is the process of collecting data via drones to produce outputs like orthomosaics, digital elevation models, and 3D models. This involves flying drones over a project site to capture images and gather data. The drones take high-quality photos and collect precise measurements using special sensors, which are then turned into 3D models, providing a clear view of the site for designing, building, or managing projects. Reality Capture techniques further enhance the accuracy and detail of these models, integrating data from various sources to create comprehensive representations of the site.
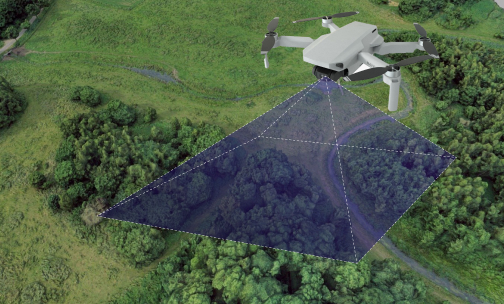
How Drone Mapping Works
Pre-Flight Planning: Before flying, the team checks the site and creates a flight plan that determines where the drone will fly, how high it will go, and what angles it will capture. This careful planning ensures all important areas are covered. Flight planning apps like OpenSky and Pix4D Capture can be used for safe flight planning and automated data collection.
Data Capture: Drones take off and capture high-resolution images and data from different angles, following a systematic flight pattern with sufficient overlap (recommended 80%) to ensure comprehensive coverage.
Data Processing: After the flight, the collected data is processed using powerful software. This step generates detailed 3D point clouds and models that accurately depict the site. Images need to be geotagged using onboard GPS, with improved accuracy achievable through Ground Control Points (GCPs), Post-Processing Kinematic (PPK), or Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) systems.
BIM Model Creation: The final step is turning the processed data into 3D models using software like Autodesk Revit. These models represent the actual conditions of the site and can be easily integrated into design and construction workflows.
Where Drone Mapping Can Help
Construction Monitoring: Keep track of projects in real-time with up-to-date data and models, helping to identify changes or issues that need attention.
Renovation and Retrofitting: Use accurate models of existing buildings to plan renovations, ensuring changes fit well with the existing structure.
Facility Management: Detailed models support efficient management and maintenance of buildings, aiding in the early identification of issues.
Surveying Complex Structures: Drones excel at capturing intricate details of complex buildings and challenging terrains, making them ideal for various surveying tasks.
Heritage Preservation: Accurately document historical sites to ensure their preservation, with data useful for restoration projects or ongoing maintenance.
Tools & Software Used
Autodesk ReCap
Converts drone data into useful 3D models for BIM software.
Pix4Dmapper
Processes aerial images into 3D models and point clouds, providing high-quality outputs.
RealityCapture
Combines different data types for accurate modeling, allowing for detailed representations.
Autodesk Civil 3D
Ideal for integrating drone scans into civil engineering projects, enhancing design capabilities.
Benefits of Drone Mapping
- Get highly detailed 3D models that reflect the true dimensions of your project site, providing reliable information for informed decisions.
- Drones can cover large areas quickly, saving time and keeping your project on schedule, resulting in faster delivery of important data.
- This service is often more affordable than traditional surveying methods, especially for larger projects, helping save money while delivering high-quality results.
- Drones can access difficult or dangerous spots without putting your team at risk, reducing the need for manual inspections in hazardous areas.
- The collected data fits seamlessly with popular BIM software, making it easy to incorporate into existing workflows.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
In Scan to BIM, drones capture high-resolution images and precise measurements of a project site. This data is processed into 3D models for integration into BIM software, aiding in project design and management.
Photogrammetry involves capturing and processing aerial images to create georeferenced maps and 3D models. It is crucial for accurately interpreting spatial relationships in mapping projects.
GCPs are specific locations with known coordinates used to improve the accuracy of drone imagery. They correlate the drone data with real-world coordinates, enhancing model precision.
Flight planning ensures comprehensive site coverage by determining the drone's flight path, altitude, and image angles, maximizing data collection efficiency.
Common software includes Autodesk ReCap for creating 3D models, Pix4Dmapper for generating point clouds, and RealityCapture for combining multiple data types.
Drone mapping is beneficial for construction monitoring, renovation and retrofitting, facility management, surveying complex structures, and heritage preservation.
